
Now write the isotopic notation for carbon-14. The name carbon-14 tells us that this isotope's mass number is #14#. Isotope notation, also known as nuclear notation, is important because it allows us to use a visual symbol to easily determine an isotope's mass number, atomic number, and to determine the number of neutrons and protons in the nucleus without having to use a lot of words.Įxample 1: What is the isotopic notation for the isotope carbon-14?įrom the periodic table, we see that the atomic number (number of protons) for the element carbon is #6#. However, because different isotopes have different numbers of neutrons, they can differ in mass number, which is the sum of the protons and neutrons in the nucleus. All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons, which is the atomic number of that element.
, Who explained the behavior of positively charged particles being deflected from a metal foil as the nucleus and more. Namely, isotope, isobar, and isotone.Isotopes are atoms of the same element that differ in the number of neutrons in their atomic nuclei. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Carbon-14 (atomic number 6), the radioactive nuclide used in dating fossils, has how many neutrons, Because most particles fired at metal foil passed straight through, Rutherford concluded that. Therefore, the number of neutrons in carbon is 6.īased on the atomic number of the element, the mass number, and the number of neutrons, three things can be considered. We know that the atomic number of carbon is 6 and the atomic mass number is 12. That is, neutron number (n) = atomic mass number (A) – atomic number (Z) Thus, the number of neutrons in an element is obtained from the difference between the number of atomic masses and the number of atoms. That is, the number of atomic masses (A) = p + n Therefore, the total number of protons and neutrons is called the atomic mass number. Therefore, atomic mass refers to the total mass of protons and neutrons.Ītomic mass(A) = Nucleus mass = Total mass of protons and neutrons (p + n)Īgain, the mass of each proton and neutron is about 1amu. The nucleus is made up of protons and neutrons. Therefore, the mass of the nucleus is called atomic mass. One is a positively charged particle proton and the other is a charge-neutral particle neutron.Īlmost all the mass of the atom is accumulated in the nucleus. There are two types of particles in the nucleus. We already know that the nucleus is at the center of the atom. Relationship between the atomic mass and carbon atomic number

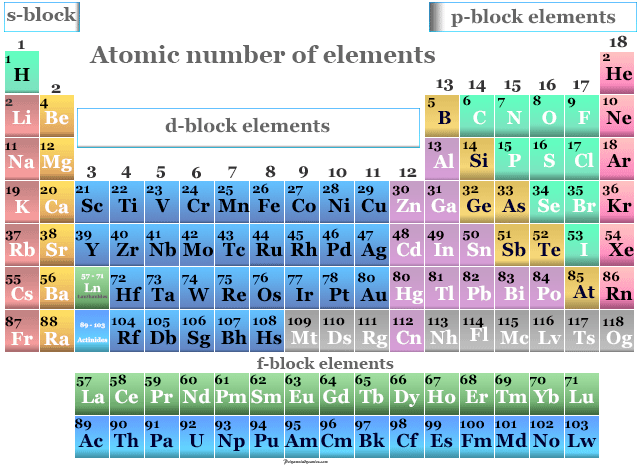
This site has published an article detailing the electron configuration of carbon that you can read if you want. To know these properties of carbon one must know the atomic number of carbon. Therefore, carbon is the p-block element. The last electron of carbon enters the p-orbital. So, the valence electrons of carbon are four. And the last shell has a total of four electrons. The last shell of carbon has four unpaired electrons, so the valency of carbon is 4. The properties of an element can be determined by electron configuration. The atomic number can be used to determine the number of electrons in an element and the exact position of an element in a periodic table.

Therefore, the number of negatively charged electrons orbiting in its orbit is equal to the number of positively charged protons in the nucleus.Ītomic number (Z) = Number of charges in the nucleus (p) Importance of the atomic number of carbonĪn atomic number is a number that carries the properties of an element. That is the total number of protons in the atomic number. We know that protons are located in the nucleus of an atom as a positive charge.
Carbon 14 atomic number serial number#
This number is equal to the serial number of the periodic table. The atomic number of the element is expressed by ‘Z’. Thus, the number of positive charges present in the nucleus of an element is called the atomic number of that element. He named that number the order of the atoms. The results of the experiment show that each element has a unique integer equal to the number of positive charges in the nucleus of that element. Scientist Henry Gwyn Jeffreys Moseley researched the X-ray spectrum of various elements from 1913 to 1914. Carbon is a p-block element and its symbol is ‘C’. Therefore, the atomic number of carbon(C) is 6. The carbon atom contains a total of six electrons and protons. The sixth element in the periodic table is carbon.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
